Water Package Code Reference¶
Pipe Class¶
Use the Pipe class to create pipe objects within your pipe network. You can add fittings to the pipe and calculate the major and minor losses through the pipe.
To see how this class can be used See Pipe Class Example on the tutorials page.
-
class
Water.Pipe(length, size, kind='PVC', sch='C900 DR-18', Re=2000)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines Pipe object to add pipe section and fittings for head loss calculations.
See data for available pipe properties.
Parameters: - length (int) – straight pipe length (ft)
- size (float) – nominal pipe diamter (in)
- kind (string) – pipe material, default ‘PVC’
- sch (variable depending on pipe material) – pipe schedule, default=’C900 DR-18’
- Re (int) – Reynolds number, default=2000
Returns: Pipe object
Return type: object
Example: >>> from Water import Pipe >>> pipe = Pipe(length=10, size=4, kind='STEEL', sch=40)
-
outer_diameter¶ outer diameter pipe property (inches)
-
inner_diameter¶ inner diameter pipe property (inches)
-
volume¶ pipe volume property (cuft)
-
area¶ pipe cross-sectional area property (sqft)
-
c_factor¶ pipe material C-factor for Hazen-Williams eq. property
-
search_material(material, coefficient=None)[source]¶ Checks sqlite database for existing material record
Parameters: - material (string) – pipe material
- coefficient (int) – Hazen Williams coefficient for major pipe losses
Returns: record(s) if one exists
Return type: list
-
add_material(material, coefficient)[source]¶ Adds a record to the hazen williams coefficient table of the sqlite db
param material: pipe material Parameters: coefficient (int) – Hazen Williams coefficient for major pipe losses
-
fitting(fitting_type=None, con_type=None, qty=1, Kvalue=None)[source]¶ Adds fitting to Pipe object’s fitting_list to add to head loss
Parameters: - fitting_type (string) – keyword from fitting dictionary, (default None)
- con_type (string) – keyword from fitting dictionary, (default None)
- qty (int) – number of fittings in pipe object, (default 1)
- Kvalue – custom loss coefficient, (default None)
Returns: appends fitting onto Pipe object’s fitting list
Example: >>> # using fitting in standard fittings dictionary >>> pipe.fitting(fitting_type='elbow_90', con_type='standard_threaded', qty=2)
>>> # creating custom fitting >>> pipe.fitting('flow meter', 'flanged', qty=1, Kvalue=1.6)
-
fitting_info()[source]¶ Returns: list of fittings currently defined in pipe object Return type: string Example: >>> print(pipe.fitting_info())
elbow_90, standard_threaded: Kvalue = 0.899, qty = 2 flow meter, flanged: Kvalue = 1.600, qty = 1
-
major_loss(flow)[source]¶ Uses Hazen-Williams equation to calculate major head loss for pipe object.
\[h_{major} = \frac{4.52 Q^{1.852}}{C^{1.852} \ d^{4.8704}} \cdot L\]Parameters: flow (int) – in gallons per minute (gpm) Returns: major head loss in ft of head Return type: float Example: >>> flow = 300 # gpm >>> pipe.major_loss(flow) 0.4272...
-
minor_loss(flow)[source]¶ Uses Minor Loss Equation to calculate minor head loss through fittings in fittings_list.
\[h_{minor} = K_L\cdot \frac{v^2}{2g}\]Parameters: flow (int) – flow in gallons per minute (gpm) Returns: minor head loss in ft of head Return type: float Example: >>> flow = 300 # gpm >>> pipe.minor_loss(flow) 3.0168...
Tank Class¶
Use the Tank class to create storage tank objects for storage related calculations. Vertical, and Horizontal cylindrical tanks are supported as well as a box reservoir.
To see how this class can be used See Tank Class Example on the tutorials page.
-
class
Water.Tank(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines Tank object to calculate storage and other tank properties.
Parameters: **kwargs (dictionary) – keyword arguments Returns: Tank object Return type: object Keyword Arguments: arguments – name: (string) - tank name diameter: (int/float) - tank diameter in ft height: (int/float) - tank height in ft, default 0 length: (int/float) - tank length in ft, default 0 width: (int/float) - tank width in ft, default 0 freeboard: (int/float) - distance from the top ring of tank to the highest water level in ft, default 0 deadstorage: (int/float) - distance from the lowest water level to the bottom of the tank in ft, defalut 0 elevation: (int/float) - tank’s base elevation in ft, default 0 shape: (string) - tank shape (‘horizontal’, ‘vertical’, or ‘box’), default ‘vertical’ operational: (int/float) - operational storage partition in ft, default 0 equalizing: (int/float) - equalizing storage partition in ft, default 0 standby: (int/float) - standby storage partition in ft, default 0 fire: (int/float) - fire-flow storage partition in ft, default 0 Example: ..code-block:
# properties for 30 ft diameter 45 ft tall cylindrical storage tank tank_data = { 'name' : 'Tank 1', 'diameter' : 30, 'height' : 45, 'freeboard' : 2, 'deadstorage' : 1, 'elevation' : 230, } tank_1 = Tank(**tank_data) # or tank object can be instantiated with individually specified parameters tank_2 = Tank(name='Tank 2', diameter=30, height=45)
-
area¶ returns cross-sectional area of tank in sqft
-
vol¶ returns dry volume of tank in gallons
-
useable¶ returns useable volume of tank in gallons
-
horizontal_vol(height)[source]¶ - calculate filled volume of horizontal tank at a specific height
- \[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}A_w &= \pi r^2 - r^2 arcos\big{(}\frac{(r-h)}{r}\big{)} + (r-h)\sqrt{2rh - h^2}\\V &= A_w \cdot L\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
Parameters: height (int/float) – water level Returns: water volume (gallons) Return type: float
-
getPercent(vol, of_vol)[source]¶ simple percentage calculation used to get the tank volume percentage of total system volume
Parameters: - vol (int/float) – tank or partition volume (numerator)
- of_vol (int/float) – total system or tank volume (denominator)
Returns: percentage of total/system volume
Return type: float
-
getHeight(vol, units='gal')[source]¶ calculates the water level in ft at given volume
Parameters: - vol (int/float) – water volume
- units (string) – units volume is given (‘gal’ or ‘cuft’)
Returns: water level in ft
Return type: float
-
getInfo(SB=0, ES=0, OS=0, FFS=0, total_vol=0, details=False)[source]¶ returns string of the current tank properties
Parameters: - SB (int/float) – system’s required standby storage in gallons, default 0
- ES (int/float) – system’s required equalizing in gallons, default 0
- OS (int/float) – system’s required operational storagein gallons, default 0
- FFS (int/float) – system’s required fire-flow storage in gallons, default 0
- total_vol (int/float) – total system volume
- details (boolean) – show storage partition details
Returns: tank object information, if details True it shows storage partition volumes and heights relative to whole system
Return type: string
-
Pump Class¶
Use the Pump class to help size pumps and compare the pump curve to a system loss curve. You can enter load for an existing pump from the built-in pump database or add new pump data. Curves can be affinitized to show where the design point would compare to pump-motor speed.
To see how this class can be used See Pump Class Example on the tutorials page.
-
class
Water.Pump(target_flow=None, target_head=None)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines Pump object to plot and/or affinitized pump curve and performance
Parameters: - target_flow (int) – target flow (gpm), default None
- target_head (int) – target head (feet of water) default None
Example: >>> from Water import Pump >>> pump_1 = Pump(target_flow=100, target_head=250)
-
search_pump(pump_model, impeller=None)[source]¶ Checks sqlite database for existing pump record
Parameters: - pump_model (string) – pump model
- impeller (float) – impeller diameter in inches, default None
Returns: pump record if one exists
Return type: list
-
add_pump(**kwargs)[source]¶ Add a pump to the sqlite3 database
param **kwargs: Use dictionary to specify parameters
type **kwargs: dictionary
keyword Arguments: model: (string) - pump model mfg: (string) - pump manufacturer flow: (list) - pump flows in acending order (gpm) mfg: (string) - pump manufacturer flow: (list) - pump flows in acending order (gpm) head: (list) - pump head in respective to flow (ft) eff: (list) - pump efficiencies respective to flow and head bep: (list) - [flow, head] for best efficiency point rpm: (int) - motor rpm impeller: (float) - impeller diameter (inches) Example: kwargs = { 'model' : 'abc123', 'mfg' : 'Acme', 'flow' : [0, 10, 20 ,30, 40, 50, 60, 70], 'head' : [300, 280, 275, 270, 250, 240, 220, 200], 'eff' : [0.50, 0.53, 0.58, 0.61, 0.66, 0.70, 0.68, 0.63], 'bep' : [220, 0.70], 'rpm' : 1800, 'impeller' : 5.125 } pump_1.add_pump(**kwargs)
-
load_pump(mfg, model, impeller=None)[source]¶ Loads pump data from sqlite3 database into pump object
Parameters: - mfg (string) – pump manufacturer
- model (string) – pump model
- impeller (float) – pump impeller size in inches, default None
Example: >>> pump_2 = Pump() >>> pump_2.load_pump('Goulds', '3657 1.5x2 -6: 3SS')
-
delete_pump(pump_id)[source]¶ deletes a pump record from the database enter pump_id of pump to be deleted
Parameters: pump_id (int) – pump id from pump table in database
-
vfd_flow¶ affinitized array of pump flows property
-
vfd_head¶ affinitized array of heads property
-
vfd_eff¶ affinitized array of efficiencies property
-
plot_curve(target_flow=None, tdh=None, vfd=True, eff=False, num_pumps=1, show=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ - creates a matplotlib plot of the pump curve.
- Default is to plot affinitized curves with full speed curve. User has option to add parallel pumps, system curve and efficiency curve. Parallel pump curves only work when vfd=False.
Parameters: - target_flow (int/float) – flow point to plot (gpm), default None
- tdh (int/float) – Total Dynamic Head (ft), default None
- vfd (boolean) – turn on/off affinitized pump curves, default True
- eff (boolean) – turn on/off pump efficiency curve, default False
- num_pumps (int) – number of pumps in parallel default 1
- show (boolean) – show plot (keep false if using in an .ipynb file), default False
- **kwargs – matplotlib.pyplot.plot keyword arguments
Returns: pump curve for pump object
Return type: matplotlib.pyplot plot
Example: Plotting a pump curve with one design point with efficiency curve
# design parameters FLOW = 100 # gpm TDH = 111 # ft head # define pump object and load pump data pump_1 = Pump() pump_1.load_pump('Goulds', '3657 1.5x2 -6: 3SS') # plot curve without affinitized curves and with efficiency curve pump_1.plot_curve(target_flow=FLOW, tdh=TDH, vfd=False, eff=True, show=True)
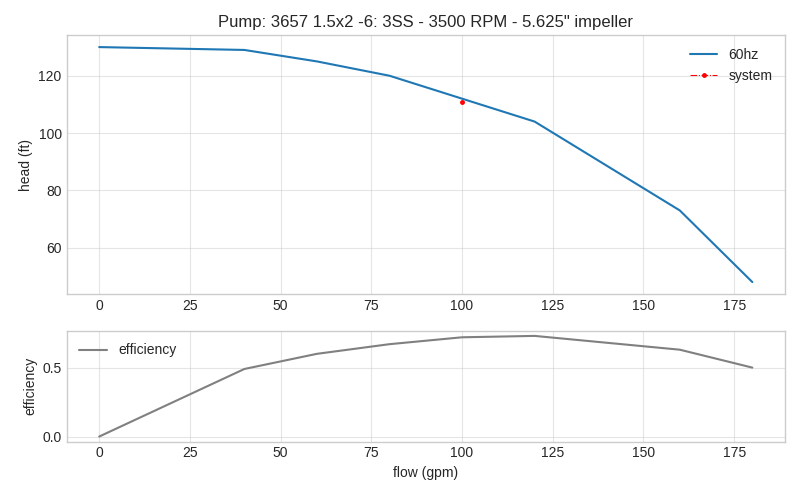
See Pump Class Example for affinitize curve functionality and how to plot a system curve along with the pump curve.
-
find_head(flow)[source]¶ - Returns head value from pump curve based on flow input.
- If flow is not a known value it will interprolate between the two closest points on the curve.
Parameters: flow (int/float) – pump flow (gpm) Returns: head value from curve data Return type: float Example: >>> Q = 125 >>> h = pump_1.find_head(Q) >>> print(h, 'ft') 100.125 ft
Genset Class¶
Use this class to create generator objects. This allows you to add electrical loads such as pump motors and lighting and calculate a total load for a genset. Load calculations are basic and should only be used to get a general genset size.
To see how this class can be used See Genset Class Example on the tutorials page.
-
class
Water.Genset(voltage, phase, capacity=None, model=None, mfg=None)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines a Genset object to calculate generator loads.
Parameters: - voltage (int) – generator output voltage (v)
- phase (int) – generator phase (ph)
- capacity (int) – generator load capaicty (kW), default None
- model (string) – generator model, default None
- mfg (string) – generator manufacturer, default None
Returns: Genset object
Return type: object
Example: >>> from Water import Genset >>> gen = Genset(voltage=480, phase=3, capacity=120, model='AB120', mfg='Acme')
-
fire_load¶ returns sum of all fire pump motor loads
-
dom_load¶ returns sum of all domestic pump motor loads
-
res_load¶ returns sum of all resistive loads
-
total_load¶ returns sum total of domestic, fire and resistive loads
-
power_factors¶ returns power factors for apparent power
-
full_load¶ returns percent genset is loaded under fire flow conditions (fully loaded)
-
normal_load¶ returns percent genset is loaded under normal conditions (domestic and resistive only)
-
add_motor_load(power, units='hp', fire=False)[source]¶ adds motor load to self.load_dict uses kVA calculation based on default power factors. All loads are saved in self.load_dict in kilovolt-amps
- 3-Phase motor power factor: 0.89
- 1-Phase motor power factor: 0.85
Parameters: - power (int/float) – motor power
- units (string) – units of power (‘hp’ or ‘kw’), default hp
- fire (boolean) – set as a fire-flow load, default False
Example: >>> gen.add_motor_load(power=5) # adding domestic pump motor load >>> gen.add_motor_load(power=25, fire=True) # adding fire-pump motor load
-
add_resistive_load(power, units='kw')[source]¶ adds resistive load to self.load_dict
for example heaters, lights, controls…Parameters: - power (int/float) – resistive load power
- units (string) – power units (‘kw’ or ‘watts’), default ‘kw’
Example: >>> gen.add_resistive_load(power=0.5) >>> gen.add_resistive_load(power=500, units='watts')
-
delete_load(load_type, index=-1)[source]¶ - deletes specific load from self.load_dict
- Prints verification when removed.
Parameters: - load_type (string) – load type keyword (‘fire’, ‘domestic’, ‘resistive’)
- index (int) – index number (use python index conventions), default -1
Example: >>> gen.show_loads() {'domestic': [4.189325842696629], 'fire': [20.94662921348315], 'resistive': [0.5, 0.5]} >>> gen.delete_load('resistive') 0.5 has been removed >>> gen.show_loads() {'domestic': [4.189325842696629], 'fire': [20.94662921348315], 'resistive': [0.5]}
-
add_consumption(consumption_list)[source]¶ Sets consumption rate for Genset object
Consumtion rates are entered as a 4 item list. Consumption values are in scfm and represent fuel consumed at 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% capacity.
Parameters: consumption_list (list) – fuel consumption at different capacities (scfm) Example: >>> consumption_list=[100, 200, 300 400] # scfm
-
size_lp_tank(min_days=4, fire_time=2, safety_factor=4, **kwargs)[source]¶ Size propane tank for a minimum number of daays of continous running. Bottles will be either 500 gal, 1000 gal or a multiple of 1000 gal bottles depending on the application.
Parameters: - min_days (int/float) – desired number of days getset should continously run default 4
- fire_time (int/float) – hours of full “fire-flow” load default 2 hrs
- safety_factor (int/float default 4) – safety factor for full load time default 4
Returns: size in gallons and quantity of propane tank needed to run min_days
Return type: tuple
Keyword Arguments: arguments –
lp_volume: (int/float) - volume of propane gas at temp in cubic feet default 36.39 lp_energy: (int/float) - energy content of propane gas in btu/gal default 91547 bottle_vol: (int/float) - starting volume of propane bottle in gallons default 500 num_bottles: (int) - starting number of bottles needed temp_factor: (int) - vaporization rule of thumb temperature factor default 2 fill_factor: (int) - vaporization rule of thumb fill factor default 60
Functions and Properties¶
Modules that contain functions and properties useful in water system design.
Tools
Tools to calculate water system design aspects
-
tools.coeffs(num_ERUs)[source]¶ C and F coefficients from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Table 3-1
Parameters: num_ERUs (int) – number of Equivalent Residential Units Returns: C and F Coefficients Return type: tuple (C, F) Example: >>> from Water import tools >>> ERUs = 1500A = \pi d^2 / 4 >>> C, F = tools.coeffs(ERUs)
-
tools.PHD(MDD, num_ERUs)[source]¶ Peak Hour Demand Calculation from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Table 3-1
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}PHD &= \frac{ERU_{MDD}}{1440}(C N + F) + 18\\\text{where:}\\PHD &= \text{Peak Hourly Demand, total system (gpm)}\\C &= \text{Coefficent Associated with Ranges of ERUs}\\N &= \text{Number of ERUs based on MDD}\\F &= \text{Factor Associated with Ranges of ERUs}\\ERU_{MDD} &= \text{Maximum Day Demand (gpd/ERU)}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]C and F coefficients are automatically calculated within PHD equation
Parameters: - MDD (int) – Maximum Day Demand (gpd/ERU)
- num_ERUs – Number of ERUs based on MDD
Returns: Peak Hour Demand (gpm)
Return type: int/float
-
tools.equalizing_storage(PHD, Qs)[source]¶ Equalizing Storage calculation from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Equation 7-1
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}ES &= 150(PHD - Q_s)\\\text{where:}\\ES &= \text{Equalizing Storage in gallons}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]Parameters: - PHD (int/float) – Peak Hour Demand in gallons per minute (gpm)
- Qs (int/float) – total source supply (gpm)
Returns: Equalizing Storage (gal)
Return type: int/float
-
tools.standby_storage(N, SBi, Td=1)[source]¶ Standby Storage calculation from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Equation 7-2
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}SB &= (N)(SB_i)(T_d)\\\text{where:}\\SB &= \text{Total Standby Storage component in gallons}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]Parameters: - N (int) – number of Equivalent Residential Units (ERUs) based on MDD
- SBi (int) – locally adopted unit SB volume in gallons per day per ERU (gpd/ERU)
- Td (int) – Number of days selected to meet water system-determined standard of reliability, default 1
Returns: Total Standby Storage (gal)
Return type: int
-
tools.calc_hp(flow_rate, head, pump_eff=0.6, motor_eff=0.9)[source]¶ Horsepower calculation for pumping water
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}hp_{water}&=(Q)(TDH)\bigg{(}\frac{1\ psi}{2.308\ ft}\bigg{)}\bigg{(}\frac{1\ hp}{1714 (psi\ gpm)}\bigg{)}\\hp_{break}&=\frac{hp_{water}}{\eta_{pump}}\\hp_{input}&=\frac{hp_{break}}{\eta_{motor}}\\\text{where:}\quad \eta_{pump} &= \text{pump efficiency}, \quad \eta_{motor} = \text{motor efficiency}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]Parameters: - flow_rate (int/float) – pump flow rate in gallons per minute (gpm)
- head (int/float) – pump head in feet (ft)
- pump_eff (float) – pump efficiency, default 0.6
- motor_eff (float) – motor efficiency, default 0.9
Returns: (water hp, break hp, input hp)
Return type: tuple
Example: from Water import tools # pumping parameters flow = 1000 # gpm head = 500 # ft of water water_hp, break_hp, input_hp = tools.calc_hp(flow, head) print(water_hp, break_hp, input_hp)
>>> 126.26262626262626 210.43771043771042 233.81967826412267
-
tools.velocity(flow, pipe_diam)[source]¶ calculate velocity through a pipe
\[v = \frac{Q}{A}\]Parameters: - flow (int/float) – flow (gpm)
- pipe_diam (float) – pipe diameter (inches)
Returns: velocity (fps)
-
tools.flow(velocity, pipe_diam)[source]¶ Calculate volumetric flowrate through a pipe
\[Q = v A\]Parameters: - velocity (int/float) – velocity (fps)
- pipe_diam (int/float) – pipe diameter (inches)
Returns: flow through a pipe (gpm)
Return type: float
-
tools.gpm2cuftps(gpm)[source]¶ Convert gallons per minute (gpm) to cubic feet per second (cuft/s)
Parameters: gpm (int/float) – gallons per minute (gpm) Returns: cubic feet per second (cuft/s) Return type: float
-
tools.cuftps2gpm(cuftps)[source]¶ Convert cubic feet per second (cuft/s) to gallons per minute (gpm)
Parameters: cuftps (int/float) – cubic feet per second (cuft/s) Returns: gallons per minute (gpm) Return type: float
-
tools.pipeDiameter(flow, velocity)[source]¶ Returns pipe diameter, given flow and velocity
\[d = \sqrt{\frac{4 Q}{\pi v}}\]Parameters: - flow (int/float) – flow in gallons per minute (gpm)
- velocity (int/float) – velocity in feet per second (FPS)
Returns: pipe diameter in inches
Return type: float
-
tools.reynolds(pipe_diam, flow=None, vel=None, viscosity=1.407e-05)[source]¶ Reynolds Number Calculation
\[Re = \frac{\mu D_h}{\nu}\]Parameters: - pipe_diam (int/float) – pipe diameter (inches)
- flow (int/float) – flow (gpm), default None
- vel (int/float) – velocity (fps), default None
- viscosity – kinematic viscosity of water (ft^2/s) default 1.407E-5 ft^2/s
Returns: Reynolds Number
Return type: int
-
tools.volume_cyl(diameter, height)[source]¶ calculate the volume of a cylinder
Parameters: - diameter (int/float) – diameter of cylinder
- height (int/float) – height of cylinder
Returns: volume of a cylinder in consistent units
Return type: float
-
tools.volume_box(length, width, height)[source]¶ calculate the volume of a box
Parameters: - length (int/float) – length of box
- width (int/float) – width of box
- height (int/float) – height of box
Returns: volume of a box in consistent units
Return type: float
-
tools.cuft2gal(cubic_feet)[source]¶ cubic feet to gallon conversion
Parameters: cubic_feet (int/float) – cubic feet Returns: gallons Return type: float
-
tools.gal2cuft(gallons)[source]¶ gallon to cubic feet conversion
Parameters: gallons (int/float) – gallons Returns: cubic feet Return type: float
-
tools.gal2acft(gallons)[source]¶ gallons to acre-feet conversion
Parameters: gallons (int/float) – gallons Returns: acre feet Return type: float
-
tools.acft2gal(acft)[source]¶ acre-feet to gallons conversion
Parameters: acft (int/float) – acre feet Returns: gallons Return type: float
-
tools.cuin2gal(cubic_inches)[source]¶ cubic inches to gallons conversion
Parameters: cubic_inches (int/float) – cubic inches Returns: gallons Return type: float
-
tools.gal2cuin(gallons)[source]¶ gallon to cubic inch conversion
Parameters: gallons (int/float) – gallons Returns: cubic inches Return type: float
-
tools.minor_loss(velocity, k_val)[source]¶ Uses Minor Loss Equation to calculate minor head loss through fittings in fittings_list.
\[h_{minor} = K_L\cdot \frac{v^2}{2g}\]Parameters: - velocity (int/float) – velocity (fps)
- k_val – K value
Returns: minor head loss (ft)
Return type: float
-
tools.kinetic_loss(velocity)[source]¶ calculate the kinetic loss term in the bernoulli equation
..math:: frac{v^2}{2g}
-
tools.ft2psi(ft_of_head)[source]¶ feet of head to pounds per square inch (psi) conversion
Parameters: ft_of_head (int/float) – feet of head Returns: psi Return type: float
-
tools.psi2ft(psi)[source]¶ return psi to feet of head
Parameters: psi (int/float) – pounds per square feet (psi) Returns: feet of head Return type: float
-
tools.hpn_size(cut_out, cut_in, num_cycles, max_flow, tank_diam, shape='horiztonal')[source]¶ Conventional hydro-pneumatic tank sizing calculation from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Equations 9-2 and 9-3
Parameters: - cut_out (int/float) – P 1 nominal pump-off pressure (psi)
- cut_in (int/float) – P 2 nominal pump-on pressure (psi)
- num_cycles (int) – max number of cycles/hour/pump (Nc)
- max_flow (int/float) – estimated max flow from 1 pump (Qp)
- tank_diam (int/float) – diameter of tank (inches)
- shape (string) – tank shape (must be ‘horizontal’ or ‘vertical’)
Returns: recommended volume for hydro-pnuematic tank
Return type: float
-
tools.bladder_size(cut_out, cut_in, num_cycles, max_flow, bladder_vol)[source]¶ Bladder Tank sizing from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Equation 9-1
Parameters: - cut_out (int/float) – nominal pump-off pressure in psi
- cut_in (int/float) – nominal pump-on pressure in psi
- num_cycles (int) – max number of cycles/hour/pump
- max_flow (int/float) – estimated max flow from 1 pump
- bladder_vol (int/float) – volume of bladder tank in gallons
Returns: number of bladder tanks
Return type: int
-
tools.air_dump_valve_size(cut_out, cut_in, tank_vol, evac_time=5, info=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ “Air Dump” valve orifice size calculation. Sizes the minimum theoretical orifice diameter of an air release valve to evaculate a volume of air in a given period of time. This function assumes a starting water level in the tank at half full and a required dump air volume when the tank is empty.
\[A = \frac{W}{C K P_1 K_b} \sqrt{\frac{T Z}{M}}\]where A = orifice area
Parameters: - cut_out (int/float) – nominal pump off pressure in psi
- cut_in (int/float) – nominal pump on pressure in psi
- tank_vol (int/float) – volume of H-PN tank in gallons
- evac_time (int) – time to empty entire tank in minutes default 5
- info (boolean) – print report default false
- **kwargs (dictionary) – keyword arguments
Returns: theoretical orifice size, if info==true then it will print a report
Return type: float
Keyword Arguments: arguments –
R: (int/float) - ideal gas constant in ftlb/Rankine default 53.35 T: (int/float) - air temperature in Rankine default 527.7 Z: (int/float) - compressibility factor default 1 C: (int/float) - gas constant based upon the ratio of specific heats default 356 K: (int/float) - coefficient of discharge default 0.975 k_b: (int/float) - backpressure correction factor default 1 M: (int/float) - molecular weight of of air in lbm/lbmol default 28.97
-
tools.pressure_relief_valve_size(cut_out, tank_vol, capacity=None, info=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ pressure relief valve sizing calculation for ASME VIII valve on a H-PN tank
\[A = \frac{W}{C K P_1 K_b} \sqrt{\frac{T Z}{M}}\]where A = orifice area
Parameters: - cut_out (int/float) – nominal pump off pressure in psi
- tank_vol (int/float) – volume of H-PN tank in gallons
- capacity (int/float) – required relieving capacity in SCFM default None (see note)
- info (boolean) – print a report of the results
- **kwargs (dictionary) – keyword arguments
Returns: returns the minimum orifice diameter of a H-PN tank
Return type: float
Keyword Arguments: arguments –
R: (int/float) - ideal gas constant in ftlb/Rankine default 53.35 T: (int/float) - air temperature in Rankine default = 527.7 Z: (int/float) - compressibility factor default 1 K: (int/float) - coefficient of discharge default 0.878 k_b: (int/float) - backpressure coefficient default 1 M: molecular weight of air in lbm/lbmol default 28.97 if capacity is None then it will use the WWS standard compressor capacity
-
tools.resistance(velocity=None, headloss=None, K=None)[source]¶ calculates resistance coefficient or headloss
Parameters: - velocity (int/float) – velocity in feet per second (FPS) default None
- headloss (int/float) – head loss in feet of water default None
- K (int/float) – resistance coefficient default None
Returns: resistance coefficient or headloss
Return type: float
-
tools.leakage(pipe_diam, test_pressure, linear_feet, hydrants=0, interties=0, valves=0, end_caps=0)[source]¶ calculates AWWA allowable leakage for a pressure test on a water main
\[L = \frac{N d \sqrt{P_{test}}}{7400}\]Parameters: - pipe_diam – pipe diameter in inches (in)
- test_pressure – test pressure in psi
- linear_feet – length of pipe being tested (ft)
- hydrants – number of hydrants default 0
- interties – number of interties default 0
- valves – number of valves default 0
- end_caps – number of end caps default 0
Returns: water leakage in gph and gpm
Return type: tuple
-
tools.makeup_water(diam_before, diam_after, depth_before, depth_after)[source]¶ Enter dimensions of frustrum or cylynder to return volume.
Parameters: - diam_before (int/float:) – container diameter before pumping
- diam_after – container diameter after pumping
- depth_before – water level before pumping
- depth_after (int/float) – water level after pumping
Returns: volume of water in a cylindrical or conical container
Return type: int/float
-
tools.wellhead_CFR(Q, H, n=0.22, t_list=[1, 5, 10])[source]¶ Returns fixed radius wellhead contribution zones (CFR) from the 2019 DOH Water System Design Manual Equation 9-1
Parameters: - Q (int/float) – pumping rate in cubic ft/yr
- H (int/float) – well open interval in ft
- n (float) – aquifer porosity default 0.22
- t_list (list) – times in years default [1, 5, 10]
Returns: radii of well contribution zones for listed years
Return type: list
-
tools.max_pump_elevation(elevation, NPSHr, Losses, SF=1.5, **kwargs)[source]¶ Returns maximum elevation pump suction can be above water level
Parameters: - elevation (int/float) – elevation of pump in ft
- NPSHr (int/float) – net positive suction head required in ft
- Losses (int/float) – suction side head loss in ft
- SF (int/float) – safety factor default 1.5
- **kwargs (dictionary) – keyword arguments
Returns: maximum pump elevation ft
Return type: int/float
Keyword Arguments: arguments –
Pb: (int/float) - barometric pressure in inches Hg default 29.92126 Tb: (int/float) - temperature in Kelvin default 288.15 R: (int/float) - R constant in lbft^2 default 89494.56 g: (int/float) - gravity in ft/s^2 default 32.17405 M: (int/float) - molar weight of air in lb/lb-mol default 28.9644 Pv: (int/float) - vapor pressure of water at 50F in feet default 0.75 Negative number indicates ft of head that must be supplied to suction line.
Positive number indicates how far pump can be above water level.
Properties of Water in SI units
- SI Properties:
- Module to assign and access the most common properties of water used in fluid mechanics in SI units
-
SI_properties.unit_info()[source]¶ Displays default unit information
- density = 999.7 kg/m^3
- specific_weight = 9807 N/m*3
- dynamic_viscosity = 1.31e-3 N*sec/m^2
- kinematic_viscosity = 1.31e-6 m^2/s
- boiling_point = 100 C
- freezing_point = 0 C
- vapor_pressure = 1.23e3 N/m*2 (absolute)
- speed_of_sound = 1481 m/s
- g = 9.81 m/s^2
Properties of Water in Imperial units
- Imperial Properties:
- Module to assign and access the most common properties of water used in fluid mechanics in english units
-
Imperial_properties.unit_info()[source]¶ Displays default unit information.
- density = 1.94 slugs/ft^3
- specific_weight = 62.4 lb/ft^3
- dynamic_viscosity = 2.73e-5 lb*s/ft^2
- kinematic_viscosity = 1.407e-5 ft^2/s
- boiling_point = 212 F
- freezing_point = 32 F
- vapor_pressure = 1.781e-1 psia
- speed_of_sound = 4748 ft/s
- g = 32.2 ft/s^2